Advantages:
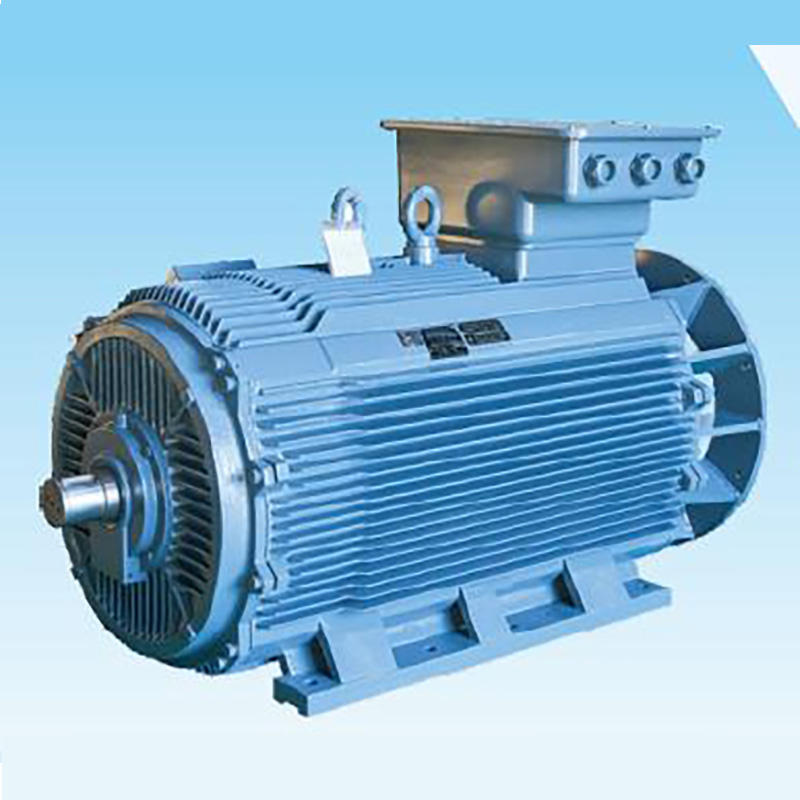
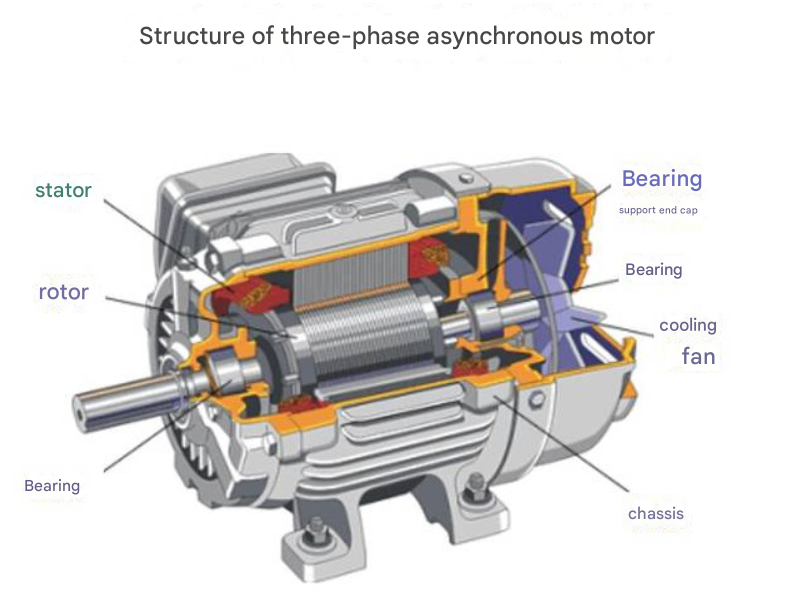
Rugged and Simple Design: Three-phase asynchronous motors (also known as induction motors) feature robust construction and require no brushes or slip rings (squirrel cage design), resulting in high reliability and low maintenance costs.
Cost-Efficient: Due to their simple design and wide range of applications, these motors have relatively low manufacturing and maintenance costs, making them an economical choice for a wide range of applications.
Self-Starting Capability: Unlike synchronous motors, three-phase asynchronous motors are self-starting, eliminating the need for additional starting mechanisms, simplifying operation and reducing complexity.
High Durability: Their brushless design and robust rotor design enable these motors to withstand harsh environments, mechanical stress, and extended operation, ensuring a long service life.
Wide Speed Range: By using a variable frequency drive (VFD), these motors can operate over a wide speed range, providing flexibility for applications requiring variable speed control.
Low Maintenance: The lack of moving electrical contacts and simple design reduce wear, minimizing maintenance requirements and downtime.
Harsh Environment Resistance: Asynchronous motors excel in dusty, humid, or chemically aggressive environments, making them suitable for demanding industrial and agricultural environments.
Applications:
Industrial Machinery: Three-phase asynchronous motors are widely used in industrial equipment such as pumps, fans, compressors, and conveyors due to their reliability, efficiency, and continuous operation capabilities.
Agricultural Equipment: These motors power irrigation pumps, grain augers, and ventilation systems in agricultural operations and are favored for their durability and ability to operate in harsh outdoor conditions.
HVAC Systems: In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, asynchronous motors drive fans, blowers, and cooling pumps, providing efficient and reliable performance in commercial and industrial buildings.
Water and Wastewater Treatment: They are used in pumps and agitators in water supply systems, sewage treatment plants, and desalination facilities, where their ruggedness and low maintenance are critical.
Manufacturing and Processing: Asynchronous motors are widely used in conveyors, cranes, and machine tools in industries such as automotive, textiles, and food processing, supporting high-volume production.
Mining and Heavy Industry: These motors drive heavy equipment such as crushers, grinders, and cranes in the mining and construction industries, leveraging their ability to withstand high loads and harsh environments.
Electric vehicles and traction systems: In some electric vehicle designs and railway traction systems, asynchronous motors are widely used due to their high efficiency and ability to provide high torque through variable frequency control.










 1BJY-324 4000LBS Capacity New Condition 12v Motor Trailer Electric Jack Parts and Accessories
1BJY-324 4000LBS Capacity New Condition 12v Motor Trailer Electric Jack Parts and Accessories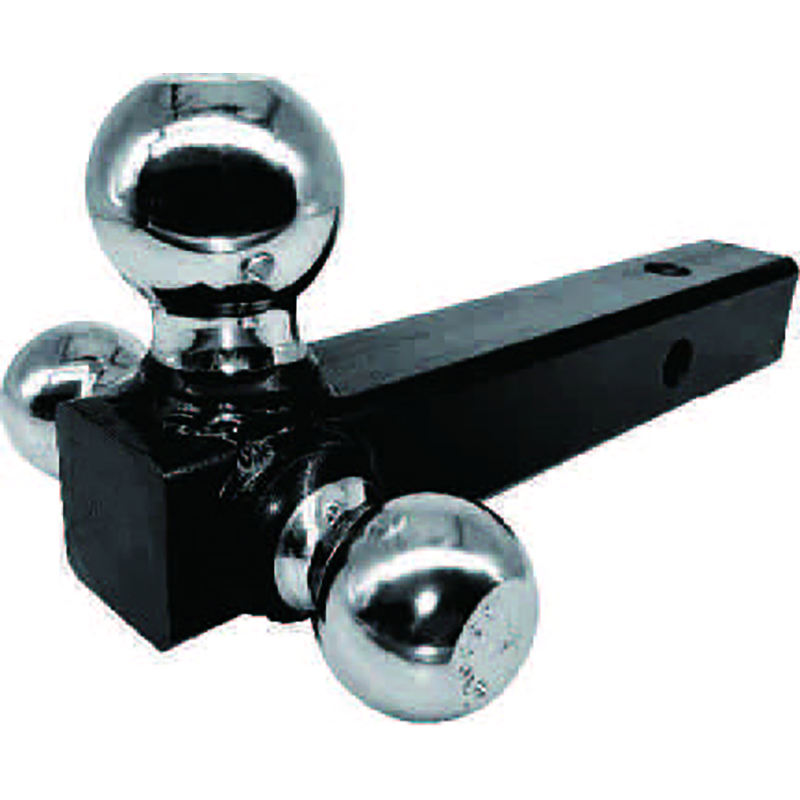 1BJY-HM-30 Chrome Ball Multi-Ball Mount New Condition Trailer Parts and Accessories with Clevis Hook Capacity 5000lbs
1BJY-HM-30 Chrome Ball Multi-Ball Mount New Condition Trailer Parts and Accessories with Clevis Hook Capacity 5000lbs 1BJY-A05 New Australian Coupler Equipped 3500KG Capacity Trailer Parts and Accessories with 50mm Ball Size
1BJY-A05 New Australian Coupler Equipped 3500KG Capacity Trailer Parts and Accessories with 50mm Ball Size Customized 40 Short Pitch Stainless Steel Extended Pin Roller Chain and Sprockets for Restaurant Industries
Customized 40 Short Pitch Stainless Steel Extended Pin Roller Chain and Sprockets for Restaurant Industries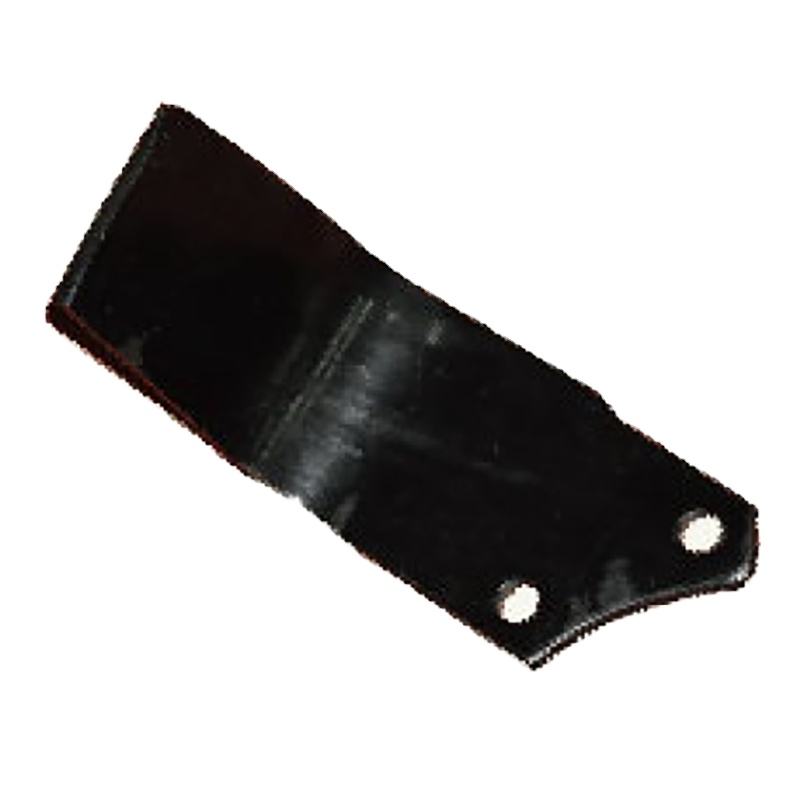 XG-4 High Quality Customized Rotary Tiller Blade Agricultural Machinery Part for Rotary Tiller Machine
XG-4 High Quality Customized Rotary Tiller Blade Agricultural Machinery Part for Rotary Tiller Machine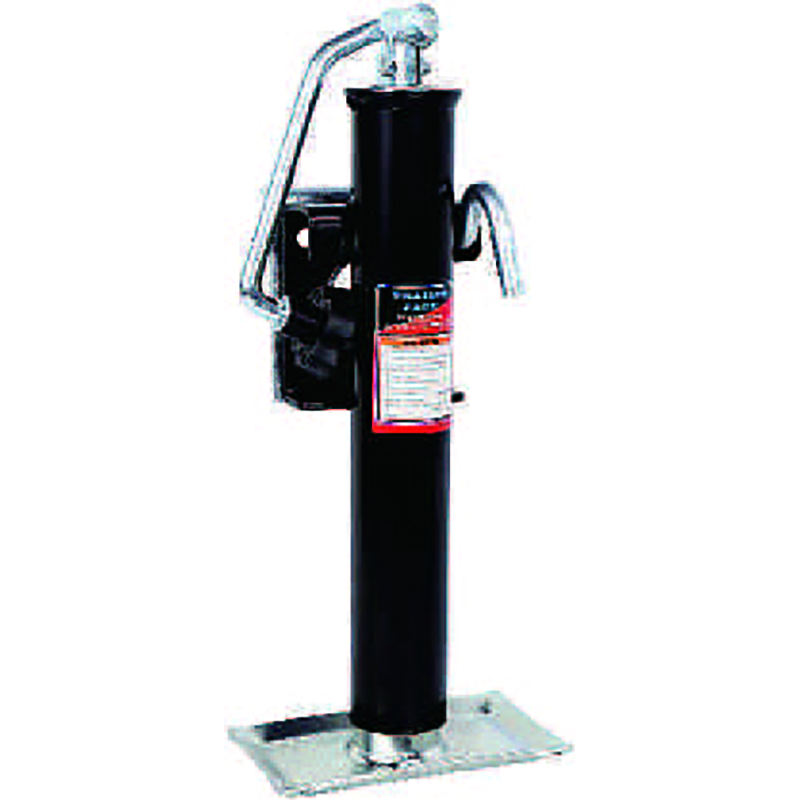 1BJY-TJ-15 New Weld-On Pipe-Mount Trailer Jack 5000LBS Capacity with Parts and Accessories Featuring Swivel Feature
1BJY-TJ-15 New Weld-On Pipe-Mount Trailer Jack 5000LBS Capacity with Parts and Accessories Featuring Swivel Feature